Applications of nanofibers in drug delivery
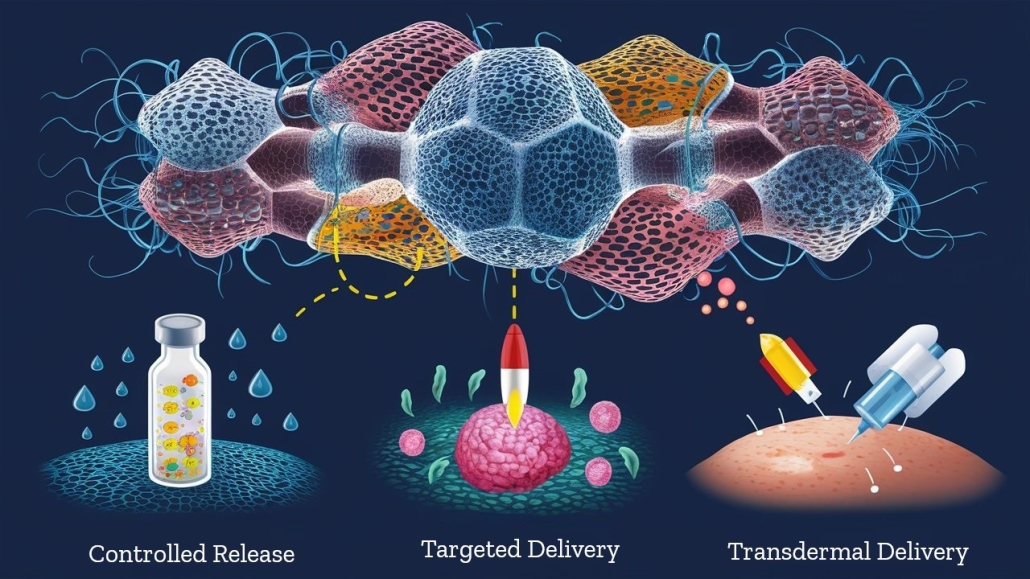
Nanofibers have emerged as a promising material in the field of drug delivery due to their unique properties, such as high surface area-to-volume ratio, tunable porosity, and the ability to encapsulate a wide range of therapeutic agents. These features make nanofibers ideal for developing advanced drug delivery systems that can improve the efficiency and targeting of treatments.
Key Applications of Nanofibers in Drug Delivery
- Controlled Release: Nanofibers can be engineered to control the release rate of encapsulated drugs, allowing for sustained delivery over a prolonged period. This is particularly useful for chronic conditions where maintaining a consistent drug level is critical. By adjusting the fiber diameter, composition, and structure, researchers can fine-tune the release kinetics to meet specific therapeutic needs.
- Targeted Delivery: Nanofibers can be functionalized with specific ligands that bind to receptors on the surface of target cells or tissues, enabling targeted drug delivery. This targeted approach minimizes the side effects on healthy tissues and enhances the therapeutic efficacy of the drug. For instance, nanofibers can be designed to target cancer cells, delivering chemotherapy agents directly to the tumor site while sparing healthy cells.
- Transdermal Drug Delivery: Nanofibers are particularly suitable for transdermal drug delivery systems, where drugs are delivered through the skin. Their high surface area and porosity facilitate the diffusion of drugs through the skin, offering a non-invasive alternative to oral or injectable delivery methods. This application is useful for pain management, hormone therapy, and other conditions requiring long-term medication.
- Wound Healing and Tissue Engineering: Nanofibers can be incorporated into wound dressings and tissue engineering scaffolds, where they not only deliver drugs but also promote tissue regeneration. For example, nanofiber-based dressings can be loaded with antibiotics or growth factors to prevent infections and accelerate healing. In tissue engineering, nanofibers can be used to deliver cells and bioactive molecules to repair or regenerate damaged tissues.
- Oral Drug Delivery: Nanofibers can also be used in oral drug delivery, where they protect sensitive drugs from the harsh environment of the gastrointestinal tract and ensure their controlled release. This approach is beneficial for drugs that are poorly soluble or have low bioavailability when administered orally.
Conclusion:
The application of nanofibers in drug delivery is a rapidly advancing field with significant potential to revolutionize how medications are administered and targeted. By enabling controlled, sustained, and targeted drug release, nanofibers offer a versatile platform for developing next-generation therapeutics that can improve patient outcomes and reduce side effects.

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!