Electroblowing process
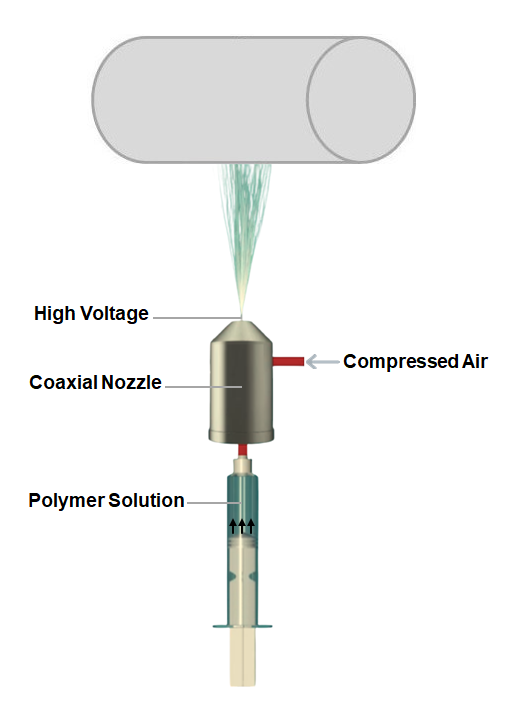
Electroblowing is an innovative technique employed in the production of nanofibers or microfibers, amalgamating the principles of electrospinning and blowing. Through the application of a high voltage, an electric field is generated, proficiently transforming a polymer solution or melt into intricate fibers.
Distinguished from electrospinning, electroblowing is executed under atmospheric conditions, rendering it particularly well-suited for the large-scale fabrication of fibers. In this method, the polymer solution or melt is extruded through a fine capillary nozzle, concurrently exposed to an intense electric field induced by high voltage. This electric field orchestrates the elongation of the fiber. Simultaneously, a controlled stream of air is directed onto the fiber during its traversal through the electric field, effectively reducing its diameter while enhancing its inherent properties.
The electroblowing process is adept at producing fibers spanning from a few microns to a few nanometers in diameter. These fibers showcase a remarkable surface area-to-volume ratio, rendering them applicable across various domains. They find utility in diverse applications, including but not limited to filtration media, battery separators, tissue engineering scaffolds, and drug delivery systems. Notably, the electroblowing process boasts cost-effectiveness and exhibits potential for seamless upscaling to meet industrial production demands.

Love it! Thanks a lot!
This work has an elegant simplicity to it, yet it holds layers of depth beneath the surface.
Thank you for your thoughtful comment. We truly value your observation—striking that balance between simplicity and depth is exactly what we aim for in our work